Introduction: CAR-T therapy is the standard of care for pts with relapsed LBCL as early as in the second line in those with early relapse or with primary refractory disease. In practice, pts who are intended to receive CAR-T, commonly require interim therapy before leukapheresis, wherein a small fraction may achieve a complete remission (CR). Having chemosensitive disease, these pts can be considered for auto-HCT. Also, there are reports indicating the efficacy of CAR-T therapy in CR pts (Strati et al., Haematologica, 2023; Wudhikarn et al., Blood Adv, 2022). We compared the outcome of pts with LBCL who received CAR-T vs. auto-HCT while in a CR.
Methods: Pts aged 18-75 years with DLBCL or primary mediastinal lymphoma who received CAR-T (between 2018-2021) or auto-HCT (between 2015-2021) while in a CR by PET or CT were included in this analysis using the data from the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) registry. Primary endpoints included progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Treatment-related mortality (TRM) and relapse rate were among the secondary endpoints.
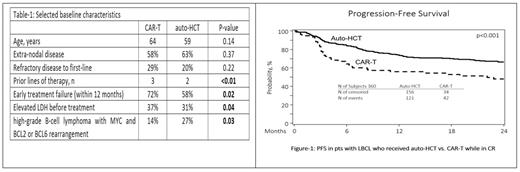
Results: We identified 360 pts with LBCL who were in a CR before receiving CAR-T (n=79, tisa-cel 53%, axi-cel 46%, and liso-cel 1%) or auto-HCT (n=281). Median follow-up was 24.7 months (range 3.3-49.4) for the CAR-T cohort and 49.7 months (range 3.0-95.4) for the auto-HCT cohort. Selected baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. CRs were confirmed by PET scan in 90% of CAR-T pts and 99.6% of auto-CAR-T pts (p < 0.01). The most common lymphodepletion regimen for CAR-T was Cy/Flu (82.3%) and the most common conditioning regimen for auto-HCT was BEAM (77.6%). Thirty-seven (13.2%) of auto-HCT pts had a later CAR-T but no pts from the CAR-T cohort had subsequent auto-HCT.
In univariate analysis, treatment with CAR-T was associated with a higher rate of relapse at 2 years (48% vs. 27.8%; p < 0.001), a lower rate of 2-year PFS (47.8% vs. 66.2%; p < 0.001) and lower 2-year OS (65.6% vs. 78.9%; p=0.037). There was no difference in rates of 2-year TRM (4.1% vs. 5.9%; p=0.673). Similarly, focusing on patients with early (12 months) treatment failure (CAR-T =57 and auto-HCT=163), treatment with CAR-T was associated with a higher 2-year relapse rate (45.9% vs. 22.8%; p <0.001) and an inferior 2-year PFS (48.3% vs.70.9%.; p <0.001) compared to auto-HCT (figure-2) while there was no difference in 2-year OS or TRM.
In the multivariable analysis of outcomes, treatment with CAR-T was associated with higher risk of relapse (HR 2.18; p < 0.0001) and an inferior PFS (HR 1.83; p=0.0011) compared to auto-HCT. There was no difference in the risk of TRM (HR 0.59; p=0.36) or OS (HR 1.44; p=0.12).
Conclusions: In pts with relapsed LBCL who achieve a CR, treatment with auto-HCT is associated with a lower relapse rate and an improved PFS compared to CAR-T, including in pts with early treatment failure (within 12 months). These results are in line with previously reported improved clinical outcomes with auto-HCT compared to CAR-T in pts in partial remission (Shadman et al. Blood, 2022). The data support utilization of auto-HCT in pts with relapsed LBCL achieving a CR.
Disclosures
Shadman:ADC therapeutics: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genmab: Consultancy, Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Consultancy; Vincerx: Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Fate Therapeutics: Consultancy; MorphoSys/Incyte: Consultancy, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Research Funding; BeiGene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Mustang Bio: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; MEI Pharma: Consultancy; Regeneron: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding. Herrera:Genentech/Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Tubulis GmbH: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Allogene Therapeutics: Consultancy; Karyopharm Therapeutics: Consultancy; Genmab: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Adicet Bio: Consultancy; Caribou Biosciences: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Research Funding; AstraZeneca/MedImmune: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy, Other: Travel/Accommodations/Expenses, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy; Regeneron: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding. Sauter:Juno Therapeutics, Celgene/BMS, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Precision Biosciences, Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi-Genzyme and NKARTA.: Research Funding; Kite/a Gilead Company, Celgene/BMS, Gamida Cell, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Ono Pharmaceuticals, MorphoSys, CSL Behring, Syncopation Life Sciences, CRISPR Therapeutics and GSK.: Consultancy. Hamadani:CRISPR: Consultancy; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Genmab: Consultancy; BeiGene: Speakers Bureau; AstraZeneca: Speakers Bureau; Caribou: Consultancy; Myeloid Therapeutics: Honoraria; Incyte: Consultancy; Gamida Cell: Consultancy; Genentech: Honoraria; ADC therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Kadmon: Consultancy; Legend Biotech: Consultancy; MorphoSys: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; SeaGen: Consultancy; Astra Zeneca: Speakers Bureau; BeiGene: Speakers Bureau; Sanofi Genzyme: Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Research Funding; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Omeros: Consultancy; Genmab: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal